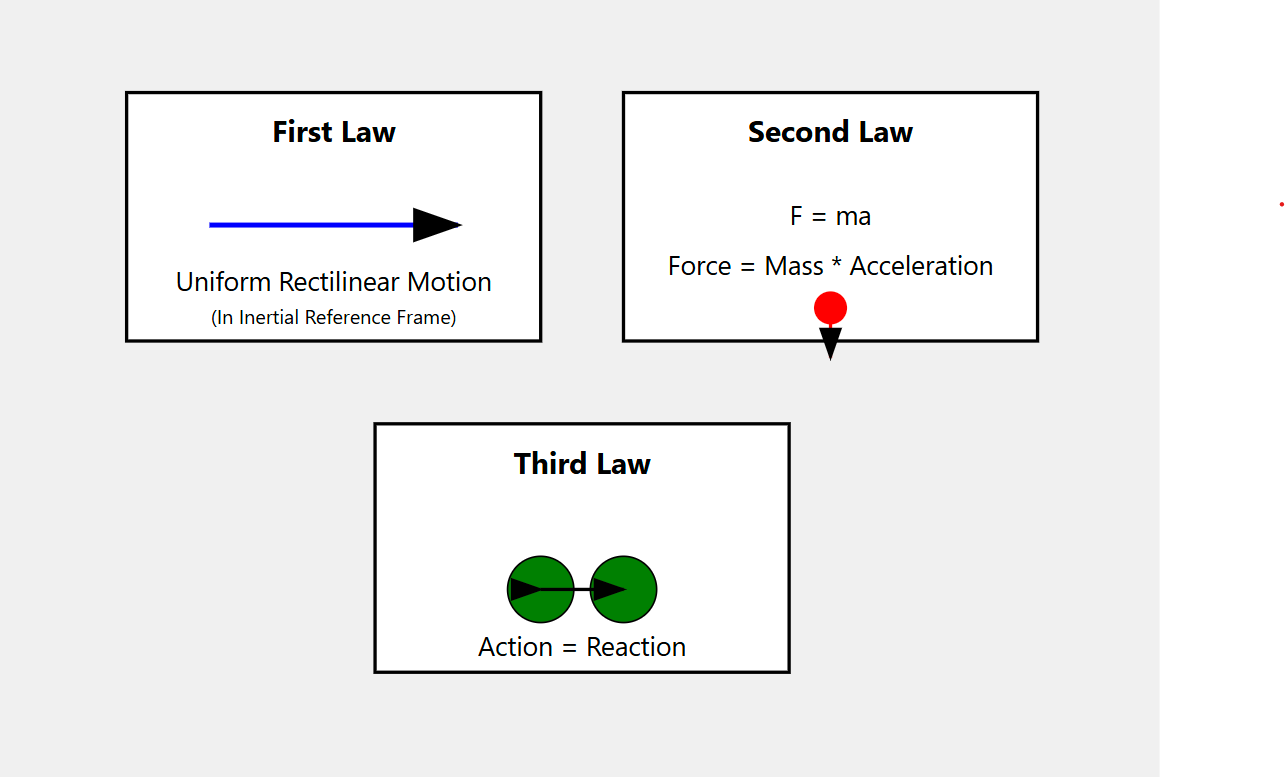
Newton’s Laws – Most Common Misconceptions
Newton's laws of dynamics form the foundation of classical physics and are an integral part of school education. Unfortunately, they are often presented in a simplified, and even erroneous manner, which can lead to misunderstandings and difficulties in deeply comprehending these fundamental principles. In this article, we will discuss the classic laws of dynamics, highlighting the frequent errors and simplifications encountered in schools and everyday reasoning.