Polarization (in physics) is limiting transverse wave vector vibrations to some direction. For non-polarised electromagnetic waves, such as visible light, the electric field vibrates in all directions perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. The electric field can be limited by reflection or passing through some materials (like special polymer grid or smooth water surface). Linear polarisation occurs when electric vector of electromagnetic wave is limited to one direction after interaction with matter. It is also possible to rotate the polarization plane, when light passing through optically active substances. In a circularly polarized light, the end of the electric vector draws a screw line around the direction of the light wave propagation. A specific case is elliptical polarization, where the electric vector also rotates around the direction of the wave propagation (like circular polarization), but its amplitude changes. The projection of the electric vector on a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation draws an ellipse.
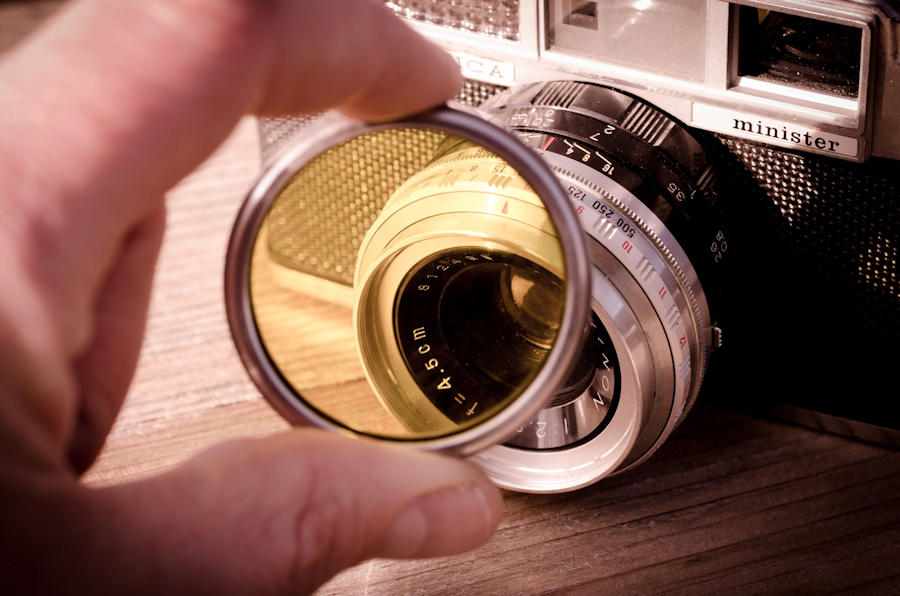

What is polarization of light?
You May Also Like
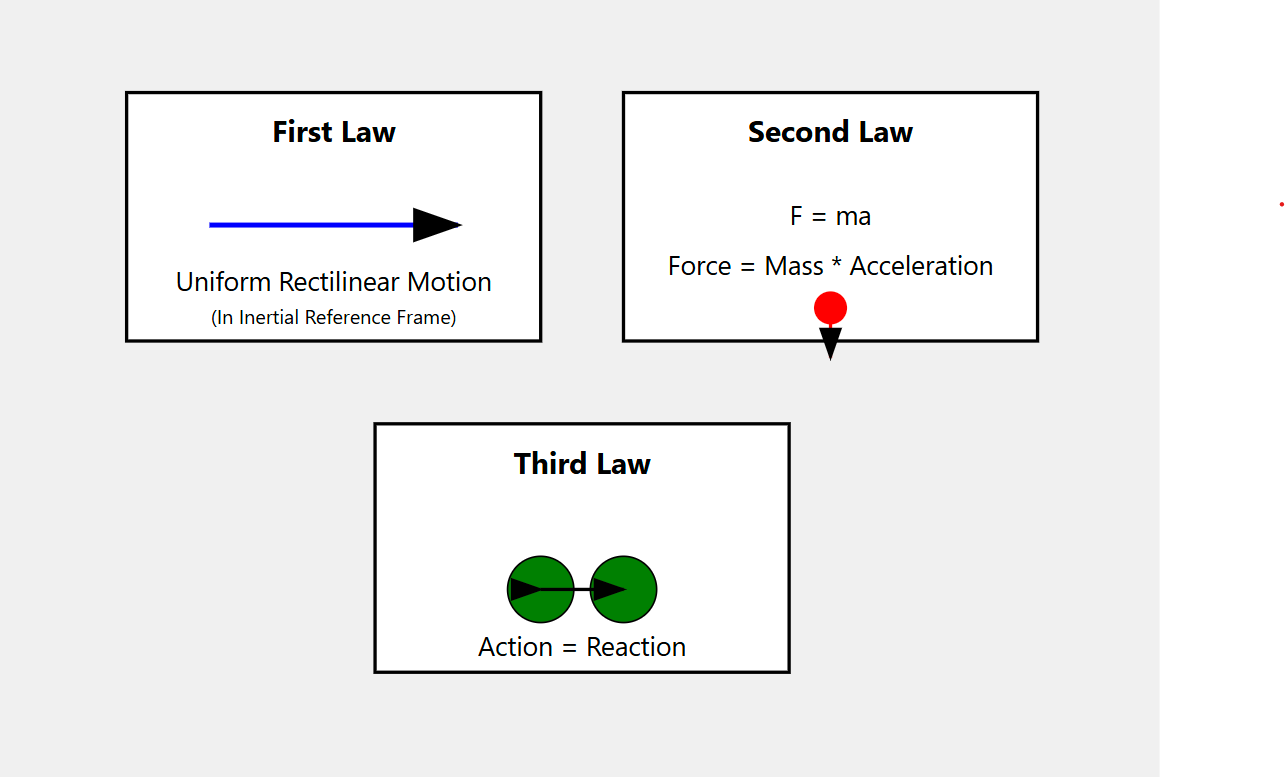
Newton’s Laws – Most Common Misconceptions
2024-12-15
Electric field – basic information
2020-08-05
Huygens–Fresnel principle
2020-02-27